- Analyzers
- Optics & Sources
- Technologies
- Support
- About
Parallel Beam X-Ray Diffraction Instrumentation for Crystalline Phase and Structure Measurements
For most samples, the aim of X-ray diffraction analysis is to identify the crystalline phases present. Phase identification is accomplished by comparing the positions and intensities of the material’s X-ray diffraction peaks against a large library of “standard” diffraction data of known crystalline materials. In this way, the different phase components of the sample can be identified. Additionally, phase transformations can also be monitored by looking for changes in the diffraction pattern of a material over time as the sample is exposed to different conditions or stresses.
Parallel beam X ray diffraction instrumentation using polycapillary collimating optics can be used to enhance phase XRD analysis of materials. Due to the insensitivity of parallel beam XRD to sample geometry and displacement errors, minimal sample preparation is required for phase analysis of samples. For the same reasons, the technique can be used to monitor phase and structure changes in an on-line system. Furthermore, through use of a polycapillary collimating optics, the parallel beam XRD system can be combined with a low power X-ray source, reducing instrument size and power requirements for in-line phase or structure measurements.
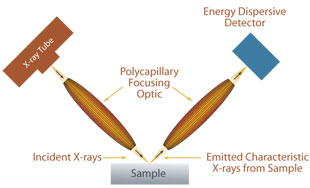
Parallel Beam X-ray Diffraction geometry using polycapillary collimating optics. This technique has been successfully used in process applications for phase distribution measurements in the pharmaceutical and steel industries.

